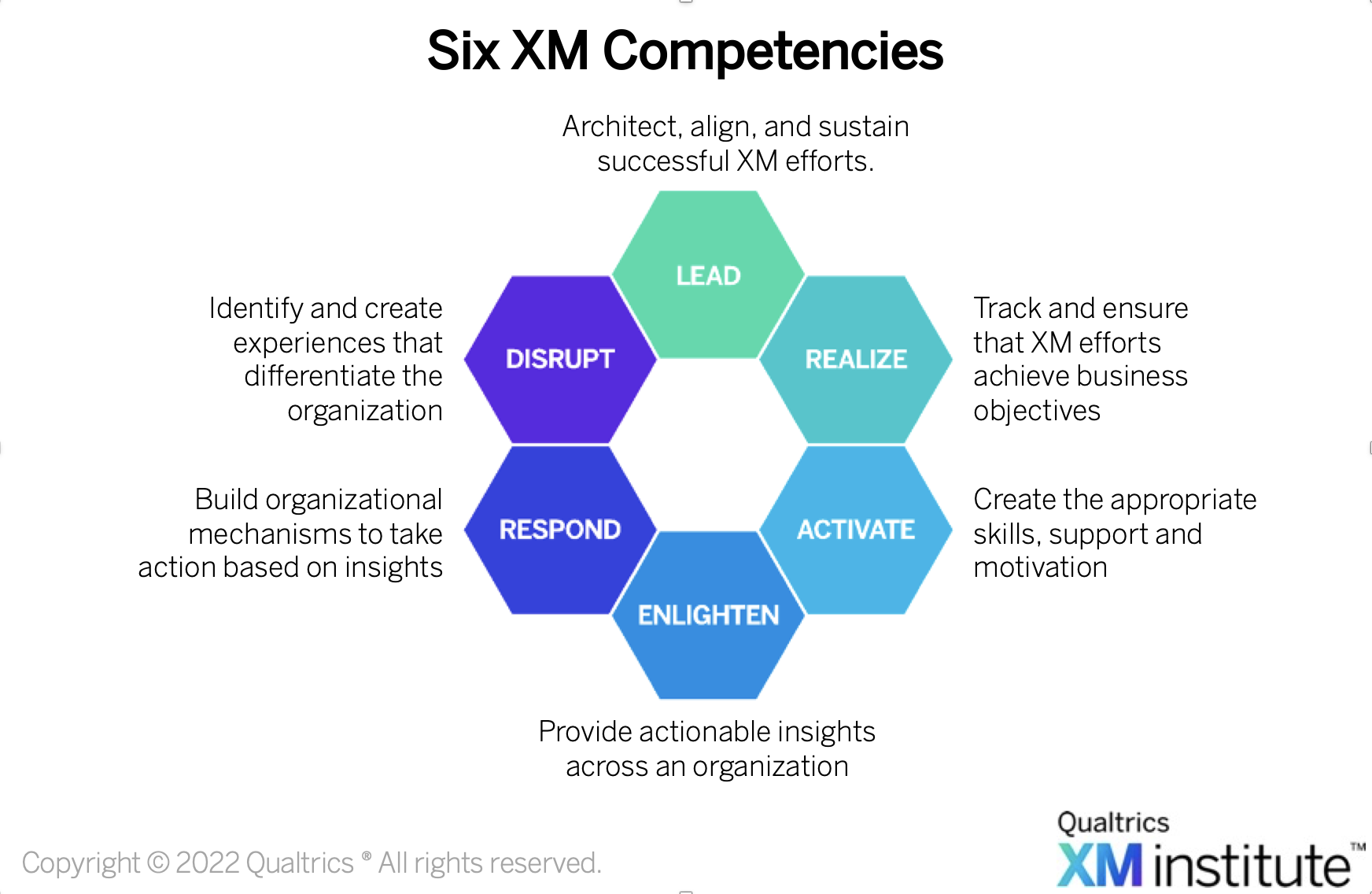
Organizations often discuss two types of loops for taking action on feedback and insights: ”inner loop,” which is about responding to people who gave feedback, and “outer loop,” which is about fixing problems uncovered by insights. While these are good actions to take, they are only a piece of the full picture. You actually need to build four insights-driven action loops.
To fully capture value from insights, organizations need to master the Six XM Competencies, which are a key component of the XM Operating Framework. The Respond Competency deals directly with taking action based on insights.
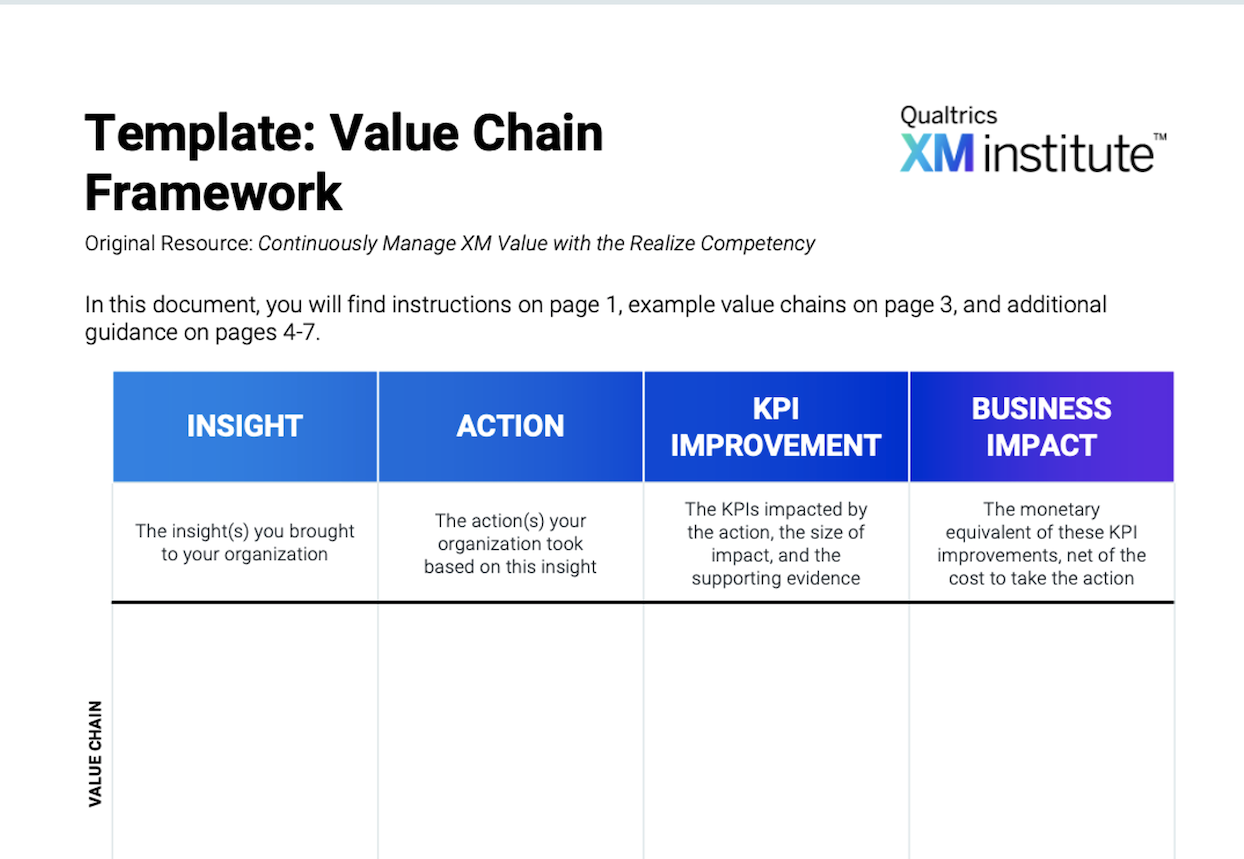
Build Four Action Loops to “Respond” to Insights
Each of the competencies has three or four associated skills. In the Respond Competency, these correspond to what we describe as four action-taking loops:
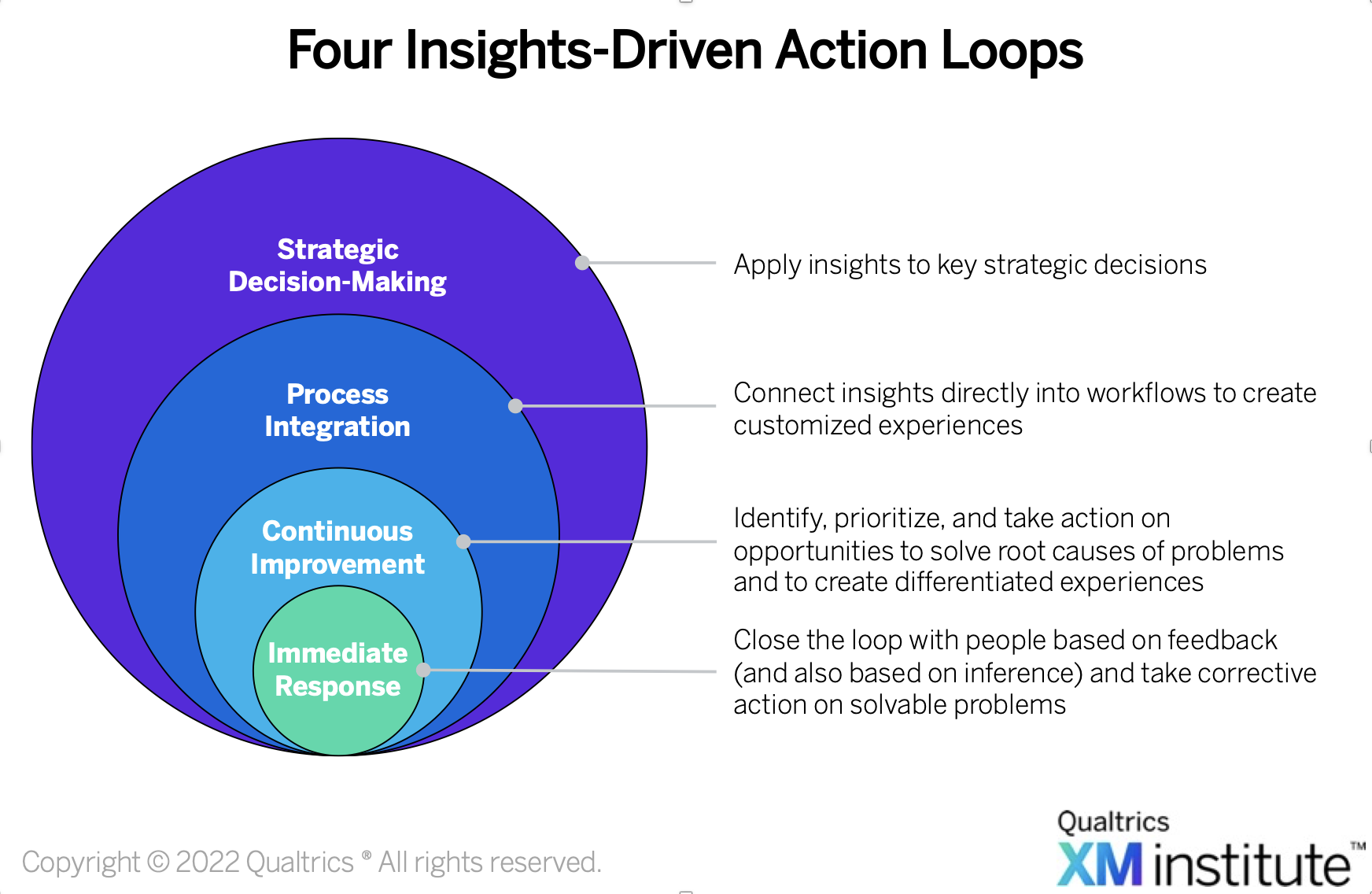
Let’s examine each of these insights-driven “loops” within the context of a restaurant that’s dealing with customer complaints about dirty bathrooms.
- Immediate Response. There are some insights that require an organization to do something right away. Let’s say a restaurant receives feedback from a customer that the bathroom was dirty. The restaurant may want to reach out to that customer to find out more and to apologize or maybe even offer a coupon for a future dining experience. While that is what’s commonly known as “closing the loop,” the Immediate Response skill also includes two other elements. First, if one customer complained about a dirty restroom, then other diners might have encountered the same experience and not provided any feedback. The organization may want to proactively do something for the diners who were there at the same time. And let’s not forget that the bathroom is dirty. So a key part of immediate response is to deal with the issue at hand and clean the bathroom right away.
- Continuous Improvement. Dealing with individual situations is valuable, but organizations need to build the capacity to learn from their insights to identify and prioritize ongoing improvements. These are often referred to as “outer loop” activities. If the restaurant chain finds that dirty bathrooms are an ongoing problem that is causing a decline in repeat business with customers, then it may want to change how it operates to ensure that it does not happen again in the future. They may develop a new process that makes someone responsible for regularly cleaning the bathrooms and create a training program to make sure that employees understand how important the bathroom experience is to customers.
- Process Integration. As insights become increasingly automated and the volume increases, organizations need to identify ways in which they can be used to trigger or customize workflows. The restaurant chain could design a process where two complaints about bathrooms within one week at a restaurant would cause a predefined heightened set of activities and mandatory training in that location. A certain level of feedback may even trigger an immediate visit and audit by the regional manager.
- Strategic Decision-Making. Insights should not only influence existing operations, they should also be used to shape key decisions about where the organization is headed and which areas to invest in. What happens if the restaurant chain finds that bathroom issues continue to be a significant problem even after ongoing improvement efforts? As part of the design of future restaurant formats, the organization may invest in new bathroom designs that either incorporate some self-cleaning elements or don’t require as much time from employees to keep them clean.
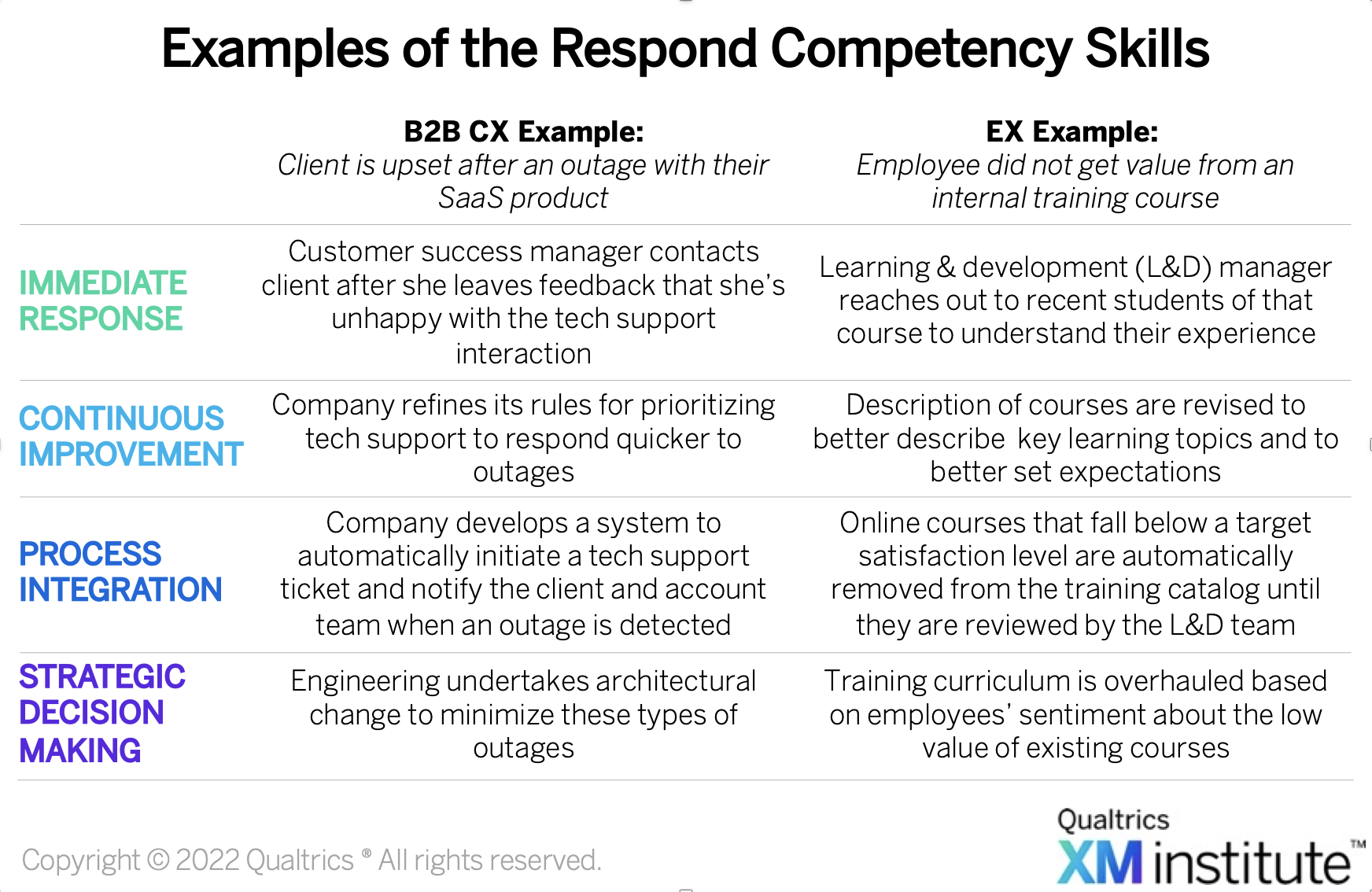
While the restaurant example above highlights the four action loops in a business-to-consumer setting, those skills can be applied to any area of Experience Management. For instance, this table provides a sense of how the Respond Skills can be applied to business-to-business customer experience (B2B CX) and employee experience (EX) settings.
The bottom line: Respond to insights by focusing on more than just inner and outer loops.
Bruce Temkin, XMP, CCXP, is the Head of Qualtrics XM Institute
Isabelle Zdatny, XMP, CCXP, is an XM Catalyst with the Qualtrics XM Institute